Aerobic Rice – (Sustainable way to grow Rice)
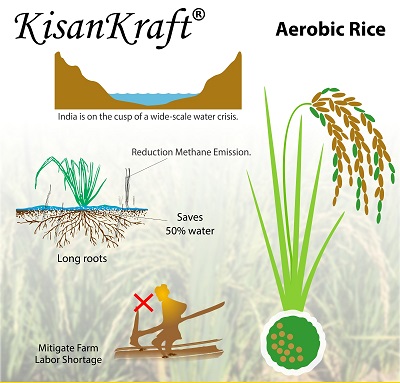
Rice is the most important food crop of India. Paddy uses largest amount of fresh water and covers 28% of the irrigated lands. Now we must produce ‘more crop per drop’ due to increasing water scarcity.
Aerobic rice is a type of rice cultivation adapted in non-puddled and non-saturated soils under irrigation just like a dryland crop such as Maize. Aerobic rice does not require standing water and is grown with 50 – 60% less water than traditional wetland rice. It helps farmer to effectively use the rainfall in the field. This is a special kind of Rice developed by combing the drought tolerant ability of upland rice with high yielding ability of lowland rice. Aerobic rice can maintain its rapid growth in the soils which are not even saturated and can yield up to 4-6 ton per hectare. Aerobic rice has been developed using conventional plant breeding techniques and does not use Genetic Engineering methods.
Just like any other dry land crops, land must be ploughed twice and brought to fine tilth before sowing. Aerobic rice can be grown in any kind of soil except black cotton. Season of sowing is as same as wetland rice. Aerobic rice seeds are sown directly with a spacing of 30 x 10 cm. It requires only 6 kg seeds per acre. Sowing can be done using seed-drills for better efficiency. Irrigation must be given immediately after sowing to saturate the soil. There is no need of standing water or puddling. Irrigation is required, only if necessary, once in 5-7 days, to keep a healthy soil moisture status. To keep field free from weeds, a pre-emergent herbicide like Pendimethalin can be applied. Weeding can be done manually or mechanically using inter-cultivators like power weeder. Aerobic rice varieties mature at around 120-135 days after sowing.
Advantages of Aerobic rice
Since Aerobic rice is direct seeded, seed rate reduces to 6-7 kg per acre compared to 25 kg per acre in irrigated rice. Many wetland rice practices e.g. nursery raising, puddling and transplanting are not required. Favorable rainfall is sufficient to grow aerobic rice just like other crops such as maize, wheat, sorghum or soybean. There is no need of standing water. Supplement irrigation is provided to keep the soil moist, if necessary. In this method, soil need not be always saturated, thereby reducing the water use to an extent of 50 – 60%. Less water does not reduce the yield. Aerobic rice saves 55% labor cost as the method is highly favorable to use dry land machineries. Being a dryland crop, aerobic rice can be inter-cropped or even mixed cropped with pulses, which helps to maintain the soil health and fertility.
Aerobic rice is an “Eco-friendly Rice” – methane emission in this method of rice production is significantly reduced and leaching of nutrients into lakes is reduced. Not having the standing water reduces outbreak of pests and diseases, which in turn reduces the consumption of pesticides. These reductions, without compromising the yield, makes aerobic rice the most cost-effective and sustainable method of rice cultivation.
Aerobic rice is the primary solution for farmers in water-scarce irrigated rice environments where water availability at the farm level is too low to grow wetland rice. Aerobic rice technology significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, thus it is better for environment.
This article was written by Mr. Sumanth Holla and Ms. Sowjanya. Both are PhD Scholars at UAS (Bangalore) and member of R&D team at KisanKraft Limited.